The heart's electrical system is a finely tuned biological circuitry that governs every heartbeat. When this electrical system works correctly, it ensures that blood is pumped efficiently to deliver oxygen and nutrients throughout the body. When it malfunctions, however, the consequences can be serious - and this is where understanding heart rhythm, cardiac rhythm disorders, and modern tools like ECG monitoring become vital for maintaining heart health.
In this article, we explore how the heart's electrical system functions, why regular rhythm matters, common rhythm disorders, and how innovations in wearable ECG monitoring - including technologies such as the Fibriart ECG patch - are transforming the detection and management of these conditions.
How the Heart's Electrical System Works
The heart has its own internal electrical system - much like a biological pacemaker - that triggers each heartbeat in a precisely timed sequence. This system ensures the coordinated contraction of the atria and ventricles, allowing blood to flow optimally throughout the body.
Here are the key components:
- Sinoatrial (SA) node: Often called the heart's natural pacemaker, it generates electrical impulses at a regular rate, typically 60-100 per minute at rest.
- Atrioventricular (AV) node: Acts as a "gatekeeper" that briefly delays the electrical signal before passing it on, allowing the atria to complete filling the ventricles with blood.
- Bundle of His and Purkinje fibers: These pathways rapidly conduct the impulse through the ventricular muscle, causing coordinated contraction and blood ejection.
This electrical cascade - from SA node -> AV node -> bundle branches -> Purkinje fibers - produces the coordinated heartbeat, which is reflected as distinct waves (P, QRS, T) on an electrocardiogram (ECG).
Why Heart Rhythm Matters
Heart rhythm refers to how regularly the heart beats and how effectively these electrical impulses are timed. A steady heart rhythm ensures that:
- Blood is pumped efficiently to vital organs like the brain and kidneys.
- Oxygen delivery meets the body's needs during activity and rest.
- Blood pressure remains stable and organ systems function optimally.
When rhythm is disrupted - that is, when electrical signals are too fast, too slow, or irregular - the heart may not pump blood effectively. This can lead to dizziness, fatigue, fainting, shortness of breath, or more severe outcomes like heart failure, stroke, or sudden cardiac arrest.
Common Heart Rhythm Disorders
Abnormal heart rhythms - broadly termed arrhythmias - occur when the normal sequence of electrical impulses is disturbed.
Here are some frequently encountered disorders:
- Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) : Rapid, irregular electrical signals in the atria leading to quivering rather than coordinated contraction. This increases the risk of stroke and heart failure.
- Bradycardia : Heart beats too slowly, often due to issues in the SA or AV node.
- Tachycardia : Heart beats too fast. This can be due to abnormal electrical pathways or triggers.
- Heart Block : Delay or complete interruption of signals between chambers, leading to uncoordinated beats.
Some arrhythmias may cause only mild symptoms, while others may have serious health consequences if left untreated. Medical evaluation is essential to determine the type and necessary intervention.
How ECG Monitoring Helps Detect Rhythm Issues
An ECG records the heart's electrical activity over time and is a cornerstone tool for identifying abnormal rhythms. Standard in-clinic ECGs capture heart activity over seconds to minutes, which can miss intermittent arrhythmias. Continuous ECG monitoring, on the other hand, records electrical data over hours, days, or weeks, improving the chances of capturing transient rhythm disturbances that might otherwise go undetected.
Continuous and Remote Monitoring: A Diagnostic Advantage
Continuous ECG monitoring is particularly valuable when symptoms are sporadic or asymptomatic. Traditional tools like Holter monitors have been used for multi-day tracking, but newer wearable ECG patches deliver enhanced comfort and longer wear times, increasing diagnostic yield.
Role of Wearable ECG Technology
Wearable heart monitors have revolutionized cardiac rhythm surveillance by enabling continuous and remote monitoring in everyday settings. These devices are lightweight, discreet, and can be worn comfortably for extended periods, capturing high-quality ECG data outside the clinic - whether during sleep, exercise, or daily routines.
Where Fibriart Solutions Fit In
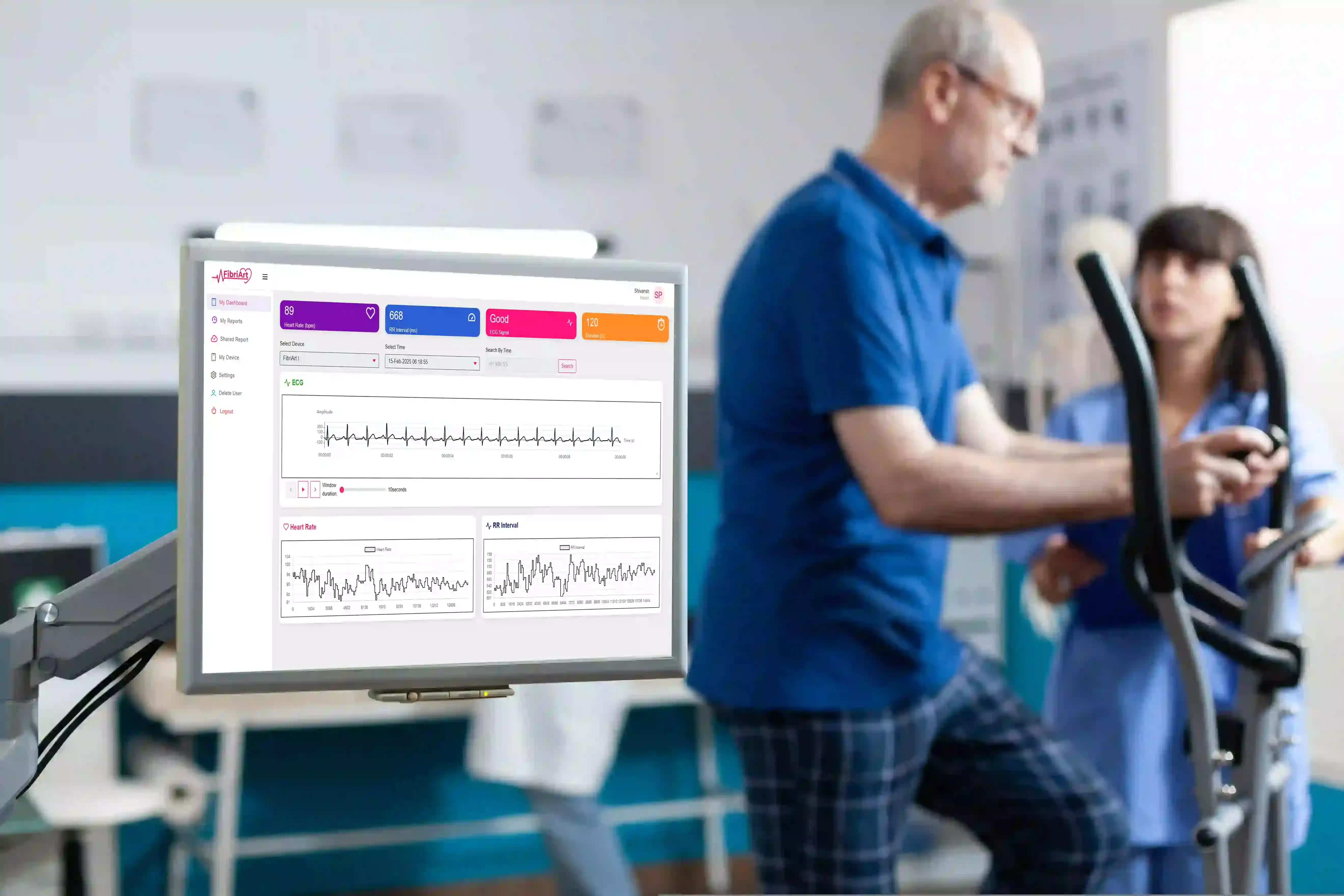
Fibriart's wearable ECG monitoring solutions leverage modern patch design and connectivity to provide clinicians and patients with reliable, medical-grade heart rhythm data:
- Comfortable, discreet ECG patches: Designed for extended continuous wear - from short-term applications up to 28 days - enabling higher chances of detecting intermittent arrhythmias compared with brief in-clinic ECGs.
- Continuous heart rhythm monitoring: With water-resistance and wearable design, patients can maintain normal activities while data is recorded.
- Remote cardiac monitoring solutions: Fibriart's patches connect to mobile platforms and cloud systems, supporting near real-time ECG insights and structured reporting for clinicians.
- Full waveform data: Capturing and analysing complete ECG signals (including PQRST segments) helps clinicians accurately identify rhythm abnormalities.
This blend of comfort, continuous monitoring, and remote accessibility enhances early detection of rhythm disorders and supports more informed clinical decision-making.
Conclusion
The heart's electrical system is fundamental to life - orchestrating each heartbeat and enabling efficient circulation. When rhythm is disrupted, symptoms may be subtle or serious, but the underlying electrical irregularities can compromise the heart's ability to function. ECG monitoring, particularly through advanced wearable technology, plays a crucial role in detecting rhythm abnormalities early and accurately.
Modern solutions like the Fibriart ECG patch are enabling continuous, patient-friendly heart rhythm monitoring that bridges the gap between traditional clinical testing and real-world, everyday cardiac surveillance. Early detection and awareness of rhythm changes empower clinicians and patients alike to manage cardiac health more effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
An arrhythmia is any disruption in the heart's normal rate or rhythm, causing the heartbeat to be too fast, too slow, or irregular.
Normal heart rhythm ensures efficient blood pumping, supporting oxygen delivery and organ function. Abnormal rhythms can reduce cardiac output and increase risk of stroke, heart failure, or other serious conditions.
An ECG records electrical activity of the heart. Continuous monitoring tracks these signals over time to detect intermittent or rare rhythm disturbances that short-term tests might miss.
Common arrhythmias include atrial fibrillation, bradycardia, and tachycardia - each reflecting irregularities in the electrical conduction process.
Wearable ECG patches allow extended periods of continuous ECG monitoring in everyday life, increasing detection of intermittent arrhythmias and enabling remote cardiac monitoring.
References
- American Heart Association - What is an Arrhythmia?
- American Heart Association - Arrhythmias Overview
- Mayo Clinic - Heart Arrhythmia: Overview & Causes
- Johns Hopkins Medicine - Electrical System of the Heart
- FibriArt - Wearable ECG Patch Technology and Features
- FibriArt - ECG Monitoring Solutions for Clinicians